Author: Suibian Translator: Kunyang Wang
Publisher: GPLP
Jun Jie, now in his 40s, is the CEO of a medical equipment company. Supposed to be a proud boast, this career has now brought him endless worry.
How so?
As a senior entrepreneur, Jun Jie has experienced a narrow escape.
Jun Jie’s first start up: Ended up with failure

Jun Jie would never forget that day in the early summer of 2008.
The day was drizzling. The clouds were combined and separated randomly.
On that day, a message turned out to be a deadly blow to his company.
At ten a.m., a telephone call turned his blood cold: a government-run hospital on the line had occurred a severe medical malpractice. It was the misdiagnosis of attending doctor that resulted in the patient’s death, and the proximate reason is that the in vitro diagnostic instrument provided by Jun Jie’s company were proved to have quality problems.
This explanation is necessary: in-vitro diagnosis(“IVD” hereinafter) refers to a diagnostic method which tests body fluids, cells and tissues as samples to acquire diagnostic information, thereby judging organism function and diseases. It has now become a significant source of diagnostic information and could provide important reference index for doctors before their medication and treatment planning. Briefly, IVD is an integral part of medical system which guarantees human health.
This hit him like a thunderbolt.
What should he do?
Despite the management of this crisis with PR department, the whole situation couldn’t be saved. Most dealers of the company started to request for return of goods. Jun Jie’s company eventually declared bankruptcy facing the ever-growing various pressure.
Jun Jie, CEO and chairman of the board, consequently had a serious illness.
A decade ago, IVD was not the mainstream of the medical market. He had really skated on thin ice starting this business.
Generally speaking, IVD could be divided into 4 categories: biochemical diagnosis, Immunologic Diagnosis, molecular diagnosis and point-of-care testing (POCT). At the moment, biochemical and immunologic are the two principal ways of IVD within China and dominate nearly two thirds of the domestic market.
The structure of the IVD industry chain mainly includes upstream raw material, IVD reagent and instrument, and downstream demand.
Uppermost upstream raw materials consist of enzyme, antigen, antibody and etc.
Downstream demand mainly comes from medical testing and blood screening. Medical testing is the most important direction of consumption. The medical institutions that provide medical testing mainly include hospitals, medical centers, disease prevention and control centers, and independent laboratories. Blood screening means the detection of blood by the blood transfusion institutions.
Due to the difficulty in research and development of upstream raw materials, most companies still rely on imports. In China, only a few companies such as Maccura and Autobio have realized the self-sufficiency of some enzymes, antigens and antibodies, but the most critical raw materials still depend on imports.
The downstream demand is directly related to the country’s economic development status and medical service level. The IVD market in developed countries such as Europe and the United States is mature, and the downstream demand is enormous. Developing and emerging economies are among the latecomers in this domain and have a large gap in terminal demand. Their market space is relatively broad.
Ten years ago, Jun Jie started his business in the field of molecular diagnostics under this background.
Of course, initially, the product was not developed by Jun Jie, but was authorized by the agency. The product was only produced and sold in China, including the linkage of instruments and reagents.
So was Jun Jie’s company.
Through the market launch, leasing and low-cost sales, they provided the IVD instruments for downstream medical institutions and distributors to establish a cooperative relationship and promote the sales of reagents. The revenue stream of the IVD industry is mainly based on the sales of reagents, and the sales of supporting reagents and consumables are driven by instruments with low gross profit rate. The immunologic diagnosis is reagent dependence and the sales of reagents account for up to 90%. It is currently the main revenue stream for IVD manufacturers.
After several years of hard work, Jun Jie’s company has grown up to a considerable size. But man proposes, God disposes. The accident has poured the last few years’ efforts down the drain.
Where Will Jun Jie go then?
Second startup: still optimistic about IVD
After half a year of rehabilitation, Jun Jie stepped out of the shadow of his company’s bankruptcy, and his body gradually recovered. However, his following choice was quite eye-popping: he decided to bounce back to IVD after the blow.
As for Jun Jie himself, if he had to give himself a reason, it was the so-called “dedication”.
“In the IVD industry, the so-called innovative medical instrument in China is mainly based on the imitation of overseas companies, and most of the companies mainly sell low-end medical instruments, especially in the IVD market. He believes that domestic medical instrument has low bargaining power and competitiveness in the middle and high-end market. He hopes to lead domestic medical instrument to the international track through a large amount of R&D investment and independent research and development. This is Jun Jie’s dream. Now, his dream just comes true.
After the Spring Festival of 2009, Jun Jie and his childhood friend William began a joint venture. This time, they decided to abandon foreign medical instrument and turn to self development.
This time, God began to save him.
After eight years of hard battle, Jun Jie’s company has now placed firmly in the domestic IVD market.
According to Evaluate Med Tech, the IVD industry accounted for 13% of the global medical instrument market in 2013 and is the largest sub-sector of the medical machinery industry. It is expected that the market share of the IVD industry will increase by 14.1% in 2020.
The global IVD industry is still in a rapid stage of development.
- From the perspective of market scale, the global IVD market has maintained a trend of steady growth in recent years. According to public data, the global IVD market scale reached US$55.4 billion in 2013 and climbed to US$59 billion in 2014. . It is expected to reach$79.3 billion with a growth rate of around 7%-8%in 2018. The continuous increase in market scale is mainly caused by the rising number of infectious diseases and chronic diseases. Continuous improvement of IVD technology is the driving force behind the development of the industry.
- From the perspective of regional distribution, the market scale of IVD is closely related to factors such as the population of the country or region, the level of economic development, and the level of medicalsecurity services. Developed countries represented by Europe.America and Japan account for about 80% of the global IVD market. However, their market lacks stamina due to maturity and it is expected that the market will expand at a rate of 1%-2% in the future. Due to the small base and large flexibility, developing countries are expected to maintain a compound growth rate of 10%-15% in the future.
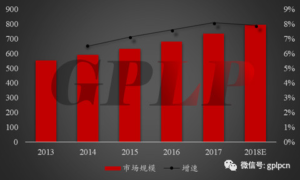
Figure 1:2013-2018 years of global in vitro diagnosis market size and growth rate (us $100 million)
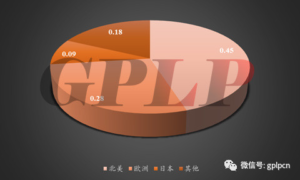
Figure 2: proportion of in vitro diagnosis market in major regions of the world in 2013
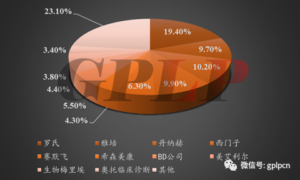
Figure 3: global in vitro diagnosis market pattern in 2016
- From the perspective of the size of the segment market, Immunologicdiagnosis accounts for the largest share of the global IVD market segment. In 2014, its proportion was about 24%, and blood glucose and POCT followed closely with 16.8% and 12.4%. Market share in emerging fields such as molecular diagnosis is relatively low, and there is much room for developmentin the future.
- From the perspective of competition structure, the global IVD market is still in an oligopolisticsituation. Of the top 10 companies in the global IVD market share, six are from the United States, three from Europe, and one from Japan. Among them, Roche accounted for the highest proportion, reaching 19.4%; Danaher followed, accounting for 10.2%; followed by Siemens and Abbott. Thetotal market share of the top ten companies in the world was as high as 76.9%.
But there’s still a long way for China to go.
This is why Jun Jie still insisted on starting business in the IVD industry even after going through bankruptcy.
“First of all, this market is really fine. I am still optimistic about it. For example, China’s per capita IVD expenditure in 2016 is less than 5 US dollars. Compared with the per capita expenditure of 25 US dollars in developed countries, our future market has huge potential. Estimated according to a mature IVD market, the potential space of China’s IVD market will exceed 200 billion yuan.
Secondly, the gap between China and the developed countries in Europe and America is really too big. I want to do a bit for IVD of China in this industry. ” Jun Jie’s reason was straightforward.
According to statistics, the development of IVD started at late 1970s, going through 3 stages including introduction, independent production and rapid development. At present, there are more than 600 companies in China engaged in IVD, but according to open data, in 2015 only 40 companies have a business scale of over 100 million, and only 13 companies with a domestic market size of more than 1%. In general, China’s IVD market is currently showing picture of a large number yet a small scale.
If taking a look at the product structure of the entire industry, people will find that China is clearly in the low-end market.
For example, the low-end market is full of early widely used detection technologies; the mid-end market has developed rapidly in recent years, and its channel advantages are obvious. In the future, there are opportunities to achieve import substitution and low-end technology substitution. The high-end market has high technical barriers. While foreign products are piled in the current Chinese market, domestic manufacturers are still in the research and development period, and will regain a certain market in the future.
In the end, 56% of the market share of the Chinese IVD market was occupied by foreign monopolies.
Foreign Giants have an early market layout in China, which has an advantage in technology, quality and brand. Therefore, 56% of the market share of China’s IVD market is occupied by these oligarchs. For example, IVD of China’s Grade-A Tertiary hospitals is basically dominated by foreign giants. Among them, Roche ranks the first, occupying 9.8% of the domestic IVD market share; Sysmex, Siemens, and Beckman occupy the second to fourth with 8.1%, 7.4%, and 6.1%, respectively.
Domestic manufacturers have huge gaps with international monopolies in terms of technology, quality and scale. Therefore, in order to survive, Chinese in-vitro diagnostic manufacturers, such as Jun Jie, can only face the low-end market at the beginning and then gradually accumulate advance products, penetrating into the high-end market.

PIC 4: Market situation of international manufacturers in China in 2015
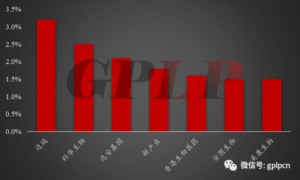
PIC 5: Market situation of domestic manufacturers in China in 2015
Knockout: how would Jun Jie break out?
Under the stimulation of two Invoice System, since 2017, China’s IVD industry has started a knockout.
Statistics show that with the gradual implementation of the two Invoice System, the distribution threshold for future IVD will be greatly improved. In addition, the company will impose strict specifications on the company scale, GSP certification and business variety, which will also eliminate most of the small and medium-sized enterprises, forming a competitive pattern in which domestic leading enterprises occupy major markets.
The IVD industry has started a frenzy of mergers and acquisitions.
Could Jun Jie’s company survive this heat of M&A?
No doubt, as a veteran of this industry, Jun Jie has taken precautions of what might happen in the future.
And this time, he bet on the closed instrument.
“future IVD industry is highly likely to develop towards closed instrument. ” That’s how Jun Jie see the future industry.
What is the so-called closed instrument?
This is equivalent to a consumer buying a brand computer, whose system and hardware combination will be more stable. While open instrument is equivalent to assembling machine, cheap indeed, but the stability of its system and hardware compatibility is not countable.
“From the perspective of the market, open instruments are in line with China’s low consumption level, and the trend will exist for a long time. But in the long run, closed instruments are the future development direction. And in a mature and highly competitive market, open instruments have been unable to meet the needs of the rapid development of the market.” Jun Jie explained.
In Jun Jie’s point of view: close instrument has two main advantages:
First, considering the matching factor of instruments and reagents, the matching reagents for the closed instruments are from the same manufacturer, which for the user, the time cost of a large number of parameter adjustments will be saved, and the detection results will be more accurate with better traceability;
Second, for manufacturers, supporting sales only need to increase the amount of instrumentation to ensure the amount of reagents. Of course, Jun Jie is not afraid of the knockout, but welcomes the coming of the elimination.
“In addition to close instruments, we will also enter POCT products market.” Jun Jie is full of confidence. In his view, with the advancement and implementation of medical reform, China’s POCT market is expected to maintain a CAGR of around 20% in the future.
It turns out that with the continuous development of medical detection technology, IVD shows two future development directions:
One is the combination of high level and high precision,
The other is to develop in the direction of simple and convenient personal health management. Of course, this direction also promotes the emergence of POCT products.
In recent years, POCT has become the first and most competitive segment of the IVD competition.
The statistics show that the global POCT market is in a stable development stage. In 2013, its market size was 16 billion US dollars. It is expected to reach 24 billion US dollars in 2018, with a compound growth rate of about 8%.
The Chinese POCT market is in the midst of rapid development due to its late start, and the market has great potential for development. According to Rncos, China’s POCT market will reach 1.43 billion US dollars in 2018.
Moreover, unlike other in vitro testing products, POCT products are characterized by a timeliness and ease of operation. The inspection objects can be monitored at any time, greatly shortening the processes of transportation, pre-processing, marking, entry and distribution time. On the other hand, because the product operation is simple and convenient, this will effectively reduce the cost of testing.
“In the future, POCT products will penetrate into every corner of our lives like digital products such as mobile computers, and gradually will become a necessity for everyone’s family health.” Despite encountering the biggest challenges in life in this industry, today’s Jun Jie is still preoccupied with IVD, and he is very optimistic about IVD. “Under the policy support and regulation, China’s IVD industry has great potential. Although the status quo will eliminate a small number of small and medium-sized production enterprises without core capabilities, the high-quality enterprises that survived thanks to R&D and innovation will become the main force in the domestic market and gradually occupy the international market.”
Trails and tribulations would always be in the way of innovation. Let’s pay tribute to innovative entrepreneurs.